Simulated Smoking Cessation Study
This project explores factors influencing successful quit attempts among baseline smokers using a simulated dataset and logistic regression modeling (N = 1,968).
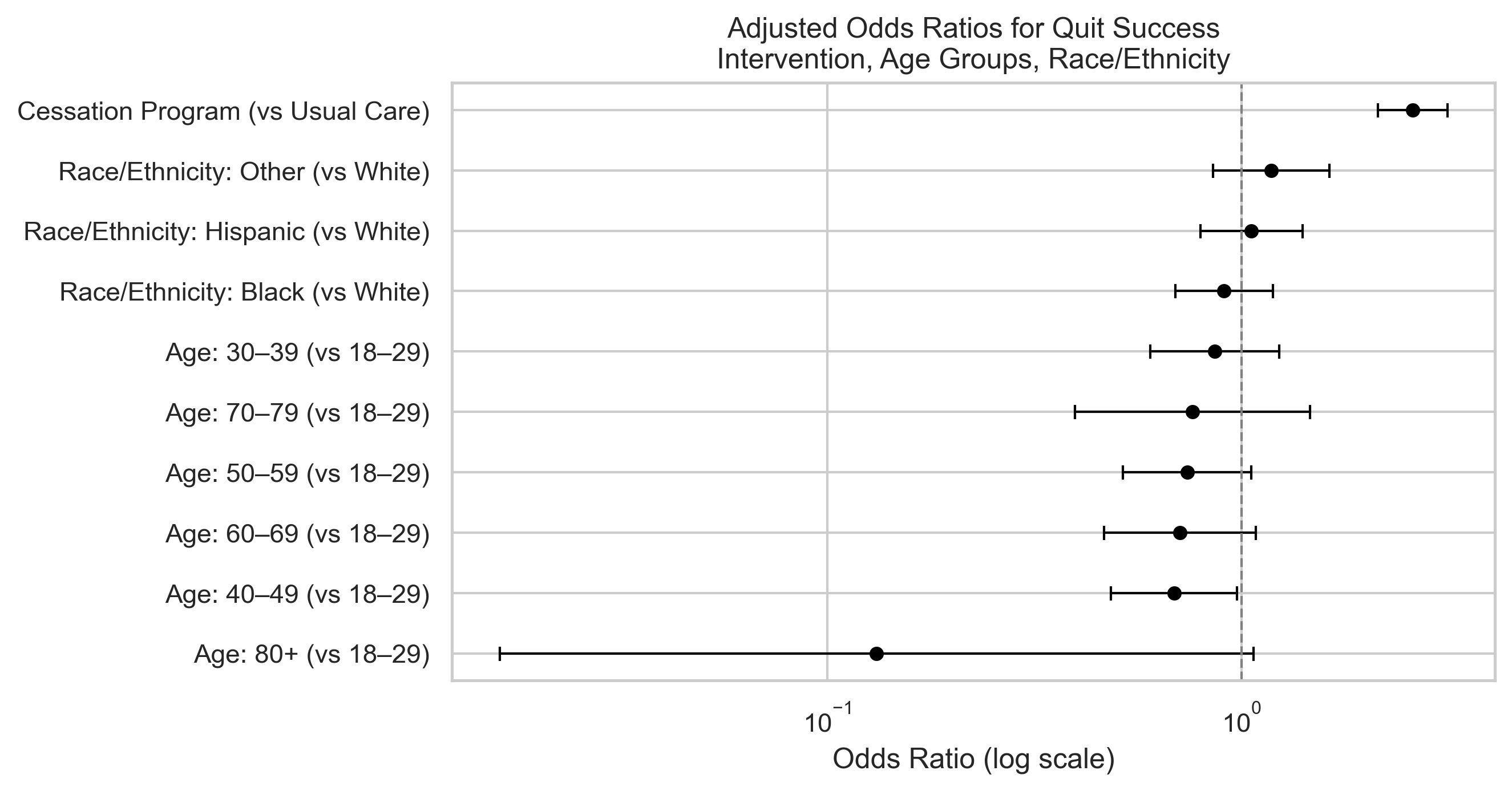
- Participation in the cessation program significantly increased quit success (OR ≈ 2.1, p < 0.001)
- Higher education and income levels were positively associated with success
- Age had a small but significant negative association
- Model was statistically significant (Pseudo R² = 0.047; LLR p < 1e–23)
Demonstrates foundational causal inference logic and statistical reporting using synthetic health data. See the README for detailed methods and modeling pipeline.
Visual Summary
Age Distribution by Education Group